[Terraform]HTTPタイプのAPI Gatewayをデプロイする

API Gatewayには2種類あって、RESTタイプとHTTPタイプがあります。RESTはよく使っていたのですが、HTTPタイプをTerraformでどう作るのかわからなかったので調べました。取り回しはあんまり変わらないのですが、サービス間の統合がRESTと結構違うのでそこが注意が必要そうです。
目次
はじめに
API Gatewayには2種類あります。
- REST APIタイプ
- HTTP APIタイプ
簡単に言うとRESTタイプのほうが高度なことができて、HTTPタイプは簡易版です。料金もHTTPタイプのほうが安く、東京リージョンの場合、月間100万リクエストあたり、HTTPが最初の3億リクエストについて1.29USD、RESTが最初の3億3000万リクエストについて4.25USDでした(2024/4時点)。およそ3.3倍ぐらいの料金差になります。
ただ、HTTPタイプのほうが新しくできたもの(V2)で、オートデプロイをサポートしていたり機能面で簡単だったりします。
詳細な違いはAWSの公式ページの比較表にあります。HTTPはWAFが対応していない+APIキーをサポートしていなかったり、一方でRESTはALBの統合はサポートしておらずNLBの統合だけだったり、それぞれ一長一短な部分があるので要件に応じて使い分ける必要がありそうです。
参考文献
* terraformでAWS API Gateway v2 (HTTP API)を使ってRESTful APIを作成する
GPT log
https://chat.openai.com/share/ab617b1f-c351-4f1f-a053-c97f03dade95
ソースコード
ディレクトリ構成
* main.tf
* lambda_function.py
main.tf
terraform {
backend "local" {
path = ".cache/terraform.tfstate"
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-1"
profile = "develop"
}
# Deploy Lambda
data "aws_caller_identity" "current" {}
data "archive_file" "lambda_archive" {
type = "zip"
source_file = "lambda_function.py"
output_path = ".cache/lambda_function.zip"
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "example" {
function_name = "HTTPAPIGatewayTestLambda"
handler = "lambda_function.lambda_handler"
runtime = "python3.12"
role = "arn:aws:iam::${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}:role/LambdaBasicExecutionRole"
filename = data.archive_file.lambda_archive.output_path
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.lambda_archive.output_base64sha256
}
# API Gateway (HTTP)
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_api" "example_http_api" {
name = "example-http-api"
protocol_type = "HTTP"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_integration" "lambda_integration" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.example_http_api.id
integration_type = "AWS_PROXY"
integration_uri = aws_lambda_function.example.invoke_arn
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_route" "example_route" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.example_http_api.id
route_key = "POST /example"
target = "integrations/${aws_apigatewayv2_integration.lambda_integration.id}"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_stage" "example_stage" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.example_http_api.id
name = "dev"
auto_deploy = true
// スロットリングの設定
default_route_settings {
throttling_burst_limit = 10 // バーストリミット
throttling_rate_limit = 5 // 秒間リクエスト数の上限
}
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "api_gw_lambda" {
statement_id = "AllowExecutionFromAPIGateway"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.example.function_name
principal = "apigateway.amazonaws.com"
// HTTP APIの場合、source_arnは必要ありません。
// HTTPS API (REST API) の場合、以下のように設定します。
// source_arn = "${aws_apigatewayv2_api.example_http_api.execution_arn}/*/*"
}
lambda_function.py
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
print(context)
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": "Hello World form HTTP API!"
}
リクエストの受取を確認するために、eventをログにダンプしている。
確認
ローカルからの実行
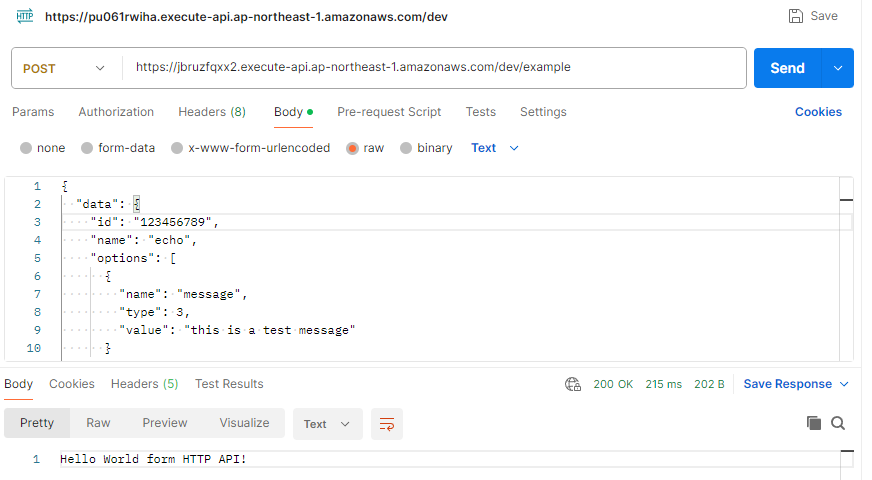
このようにうまくいく。
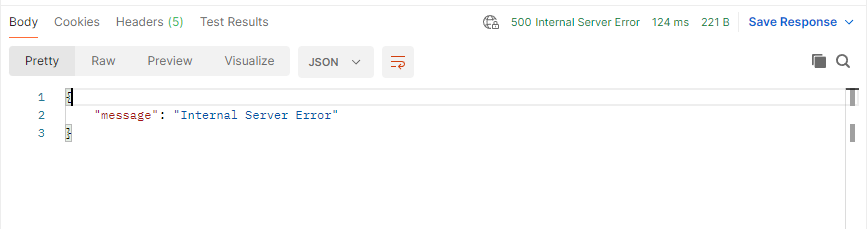
ただし、Terraformのリソースaws_lambda_permission.api_gw_lambdaを適用し忘れた場合、以下のようなエラーになる。これはLambdaのAPI Gatewayに対するパーミッションが付与されていないため。この手の付与はREST APIでも必要。
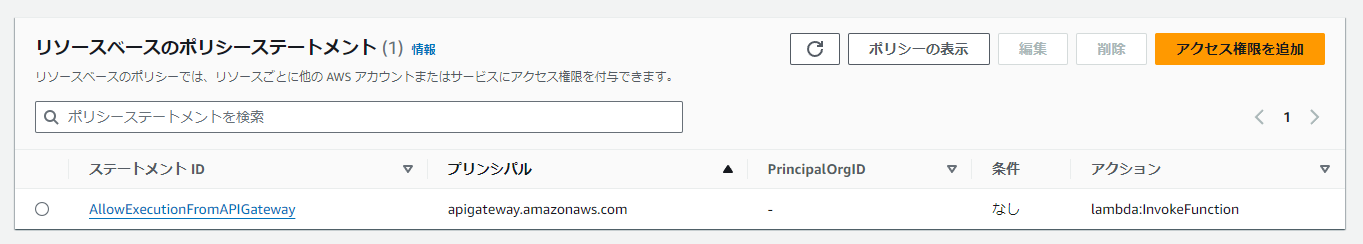
REST APIと異なり、Lambda側のトリガーのアイコンで表示されないので「あれ?」となってしまうが、Lambdaの「設定」→「アクセス権限」から確認できる。
リクエストの受け渡し
CloudWatch Logsにダンプしたものを見ると、以下のようになっていた。これは、Lambda関数内でeventをダンプしたものである。
{‘version’: ‘1.0’, ‘resource’: ‘/example’, ‘path’: ‘/dev/example’, ‘httpMethod’: ‘POST’, ‘headers’: {‘Content-Length’: ‘253’, ‘Content-Type’: ‘text/plain’, ‘Host’: ‘xxxxxxxxx.execute-api.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com’, ‘Postman-Token’: ‘ed9ce669-fd65-4d17-b1ae-438b95a82b06’, ‘User-Agent’: ‘PostmanRuntime/7.37.3’, ‘X-Amzn-Trace-Id’: ‘Root=1-6625bc47-13a39ad1426c64805b101ca3’, ‘X-Forwarded-For’: ‘XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX’, ‘X-Forwarded-Port’: ‘443’, ‘X-Forwarded-Proto’: ‘https’, ‘accept’: ‘/‘, ‘accept-encoding’: ‘gzip, deflate, br’}, ‘multiValueHeaders’: {‘Content-Length’: [‘253’], ‘Content-Type’: [‘text/plain’], ‘Host’: [‘xxxxxxxxx.execute-api.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com’], ‘Postman-Token’: [‘ed9ce669-fd65-4d17-b1ae-438b95a82b06’], ‘User-Agent’: [‘PostmanRuntime/7.37.3’], ‘X-Amzn-Trace-Id’: [‘Root=1-6625bc47-13a39ad1426c64805b101ca3’], ‘X-Forwarded-For’: [‘XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX’], ‘X-Forwarded-Port’: [‘443’], ‘X-Forwarded-Proto’: [‘https’], ‘accept’: [‘/‘], ‘accept-encoding’: [‘gzip, deflate, br’]}, ‘queryStringParameters’: None, ‘multiValueQueryStringParameters’: None, ‘requestContext’: {‘accountId’: ‘XXXX’, ‘apiId’: ‘xxxxxxxxx’, ‘domainName’: ‘xxxxxxxxx.execute-api.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com’, ‘domainPrefix’: ‘xxxxxxxxx’, ‘extendedRequestId’: ‘WmpbMizHNjMEMHg=’, ‘httpMethod’: ‘POST’, ‘identity’: {‘accessKey’: None, ‘accountId’: None, ‘caller’: None, ‘cognitoAmr’: None, ‘cognitoAuthenticationProvider’: None, ‘cognitoAuthenticationType’: None, ‘cognitoIdentityId’: None, ‘cognitoIdentityPoolId’: None, ‘principalOrgId’: None, ‘sourceIp’: ‘XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX’, ‘user’: None, ‘userAgent’: ‘PostmanRuntime/7.37.3’, ‘userArn’: None}, ‘path’: ‘/dev/example’, ‘protocol’: ‘HTTP/1.1’, ‘requestId’: ‘WmpbMizHNjMEMHg=’, ‘requestTime’: ’22/Apr/2024:XX:XX:XX +0000′, ‘requestTimeEpoch’: XXXXXXX, ‘resourceId’: ‘POST /example’, ‘resourcePath’: ‘/example’, ‘stage’: ‘dev’}, ‘pathParameters’: None, ‘stageVariables’: None, ‘body’: ‘{\r\n “data”: {\r\n “id”: “123456789”,\r\n “name”: “echo”,\r\n “options”: [\r\n {\r\n “name”: “message”,\r\n “type”: 3,\r\n “value”: “this is a test message”\r\n }\r\n ],\r\n “type”: 1\r\n },\r\n “token”: “XXXXXX”,\r\n “type”: 2\r\n}’, ‘isBase64Encoded’: False}
基本的には取り回しはRESTの場合とほとんど変わらないようだ。
管理画面
いろいろとRESTの場合と画面が変わるようだ。オートデプロイが対応しているのが良い。RESTはステージの再デプロイ周りでハマることが多かったため
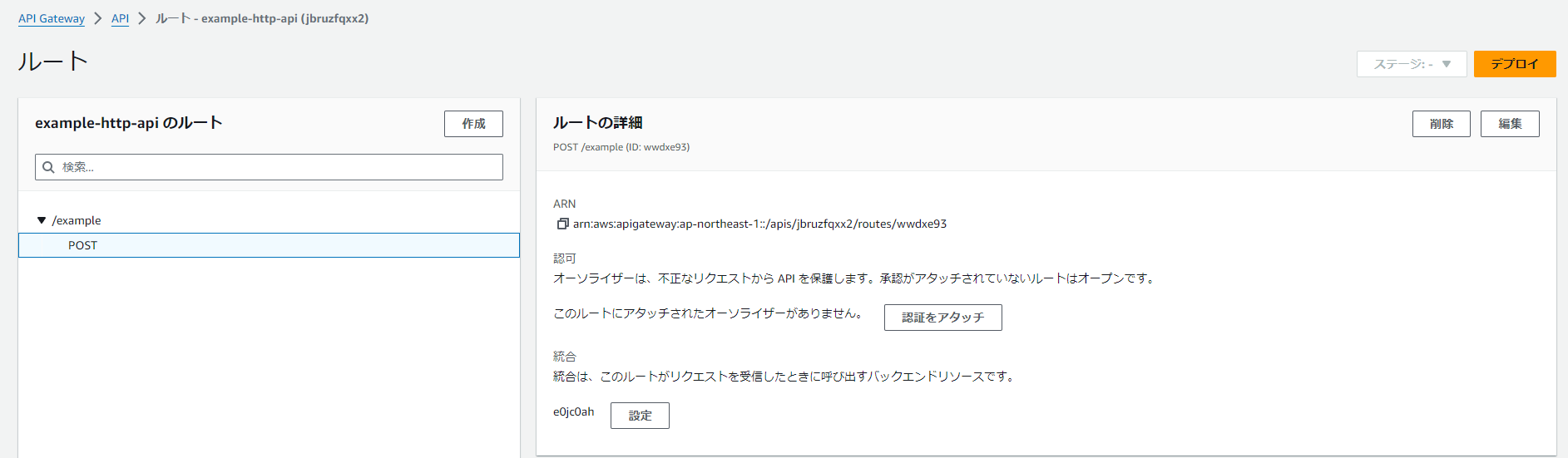
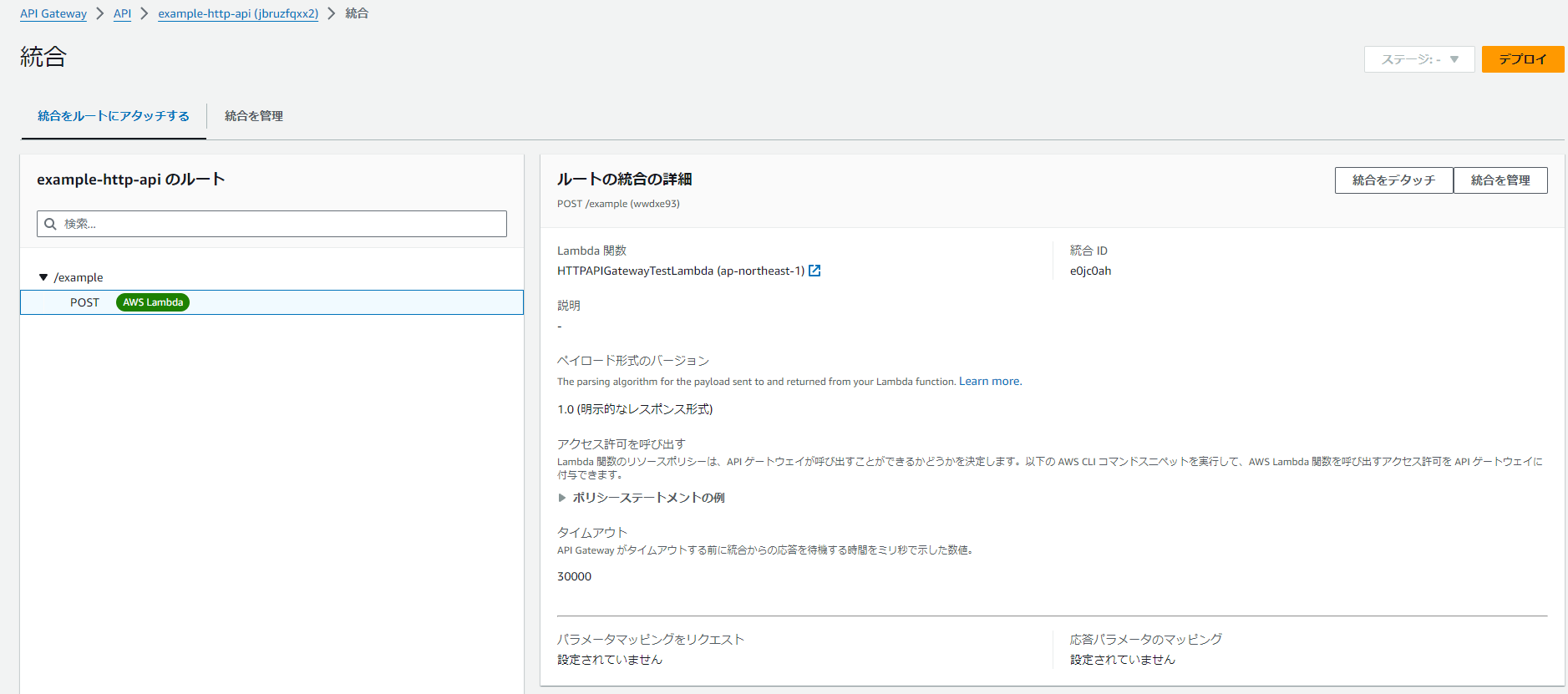
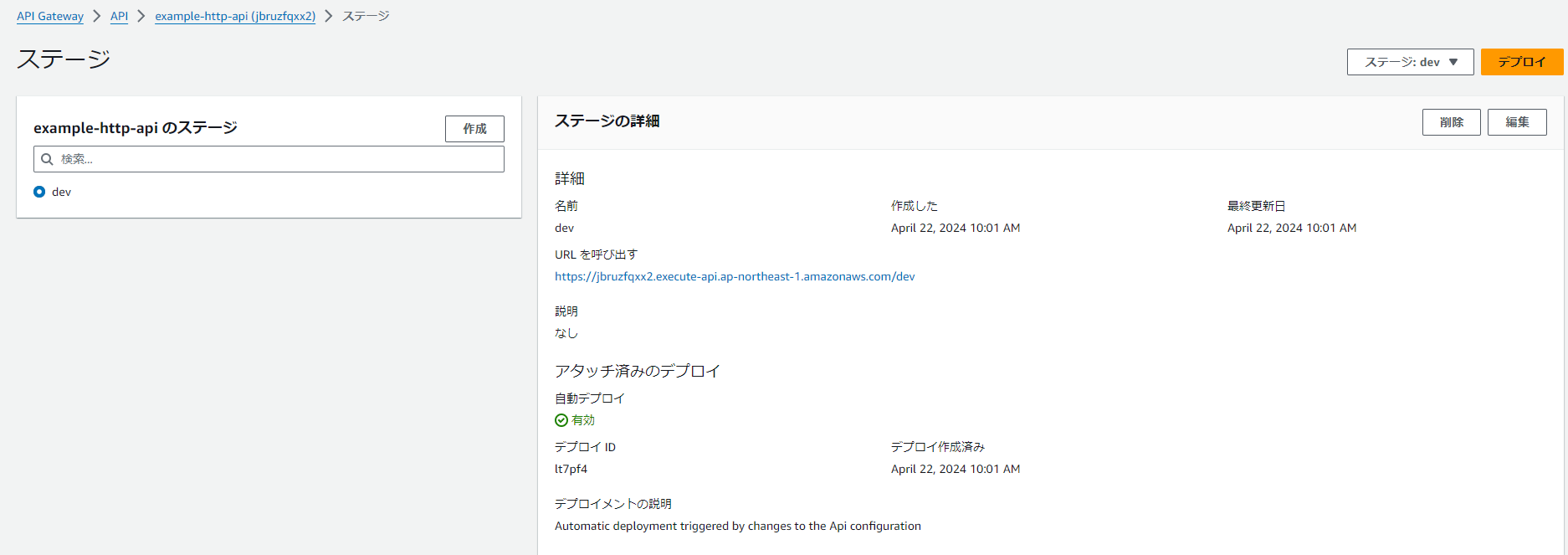
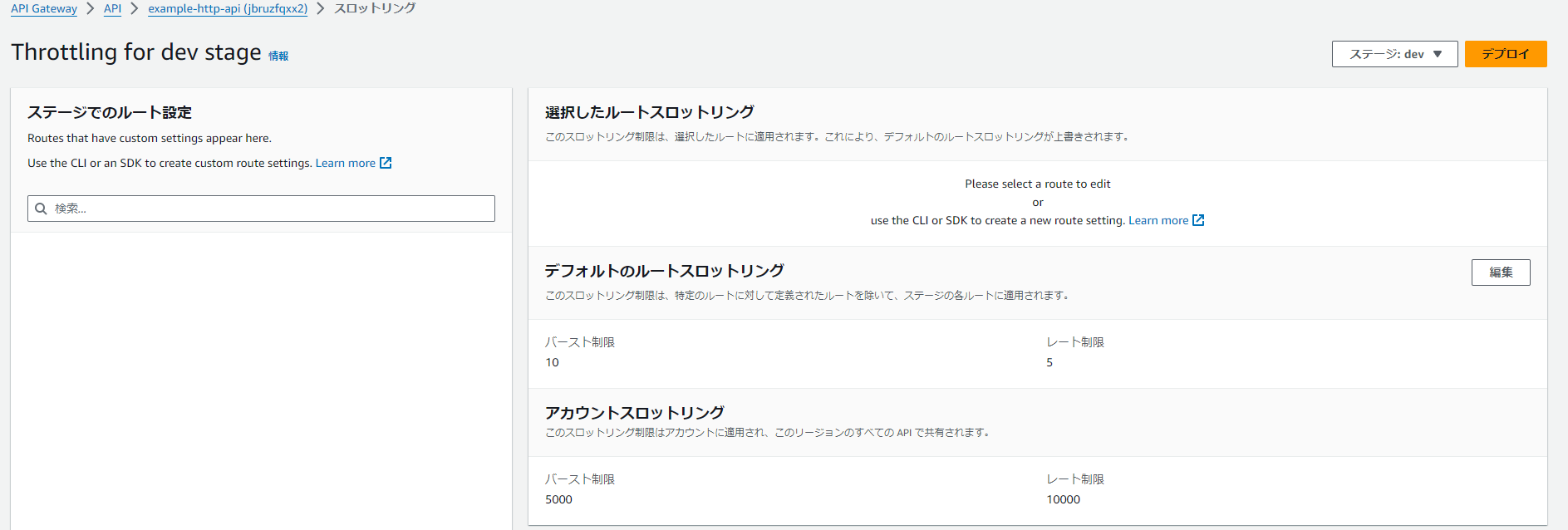
一応スロットリングは対応していた。
留意点
DiscordのAPI用のエンドポイントとして使用する場合、RESTだと動いていたが、HTTPにするとDiscord側で反応しなくなるという現象があった。バックエンドのLambdaでは処理が正常に動いているのだが、Discord側で認識しないというものだ。
これには改善方法があり、レスポンスにContent-Type: application/jsonのヘッダーを追加することで解決できる。
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'headers': { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, # 追加
'body': json.dumps(response_payload)
}
Shikoan's ML Blogの中の人が運営しているサークル「じゅ~しぃ~すくりぷと」の本のご案内
技術書コーナー
北海道の駅巡りコーナー

